
MOLT Replicator can apply userscripts, specified with the --userscript flag, to customize how data is processed and transformed as it moves through the live replication pipeline.
Userscripts are intended to address unique business or data transformation needs. They perform operations that cannot be handled by the source change data capture (CDC) stream, such as filtering out specific tables, rows, or columns; routing data from a single source table to multiple target tables; transforming column values or adding computed columns; and implementing custom error handling. Refer to Common uses.
Userscripts are written in TypeScript and run inside MOLT Replicator, giving you full programmatic control of your replication flow while maintaining type safety and consistency.
Prerequisites
- Install MOLT Replicator v1.1.4 or later for full compatibility with the userscript API.
- Install a TypeScript-compatible IDE (for example, VS Code) to write and edit userscripts with autocomplete and type-checking support.
How it works
Userscripts act as a customizable processing layer within MOLT Replicator's live replication lifecycle. They are used to intercept, inspect, and modify the flow of data as it moves from the source database to the target database, enabling full control over how rows are transformed, filtered, or applied; as well as providing the ability to run custom transactional logic against the target database.
The following diagram illustrates how userscripts fit into the replication pipeline:
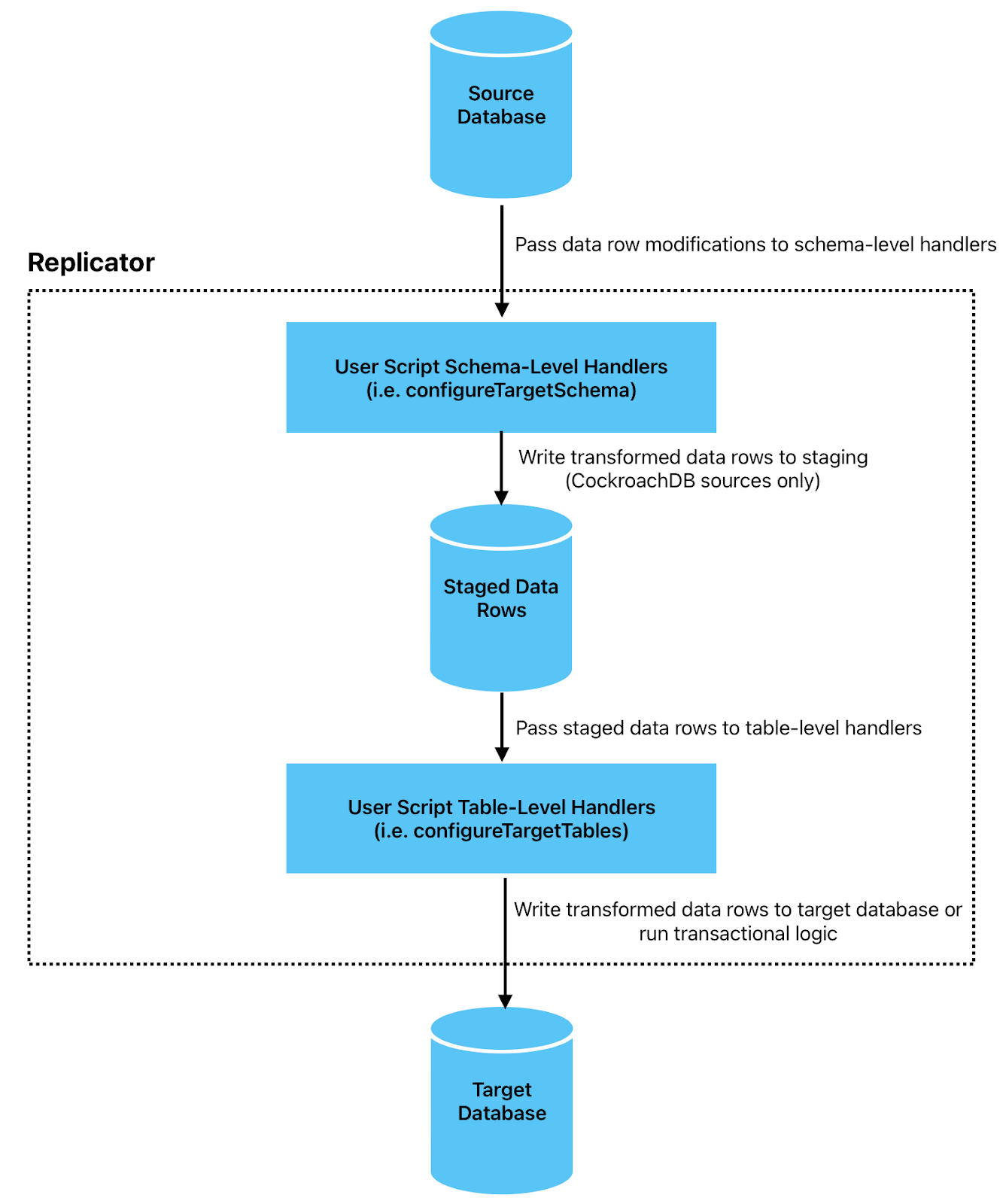
Source changefeed: Replicator continuously listens to the source database's changefeed for row modification events.
Userscript processing: When Replicator receives change events from the source database, it passes them through the userscript in two phases, in the following sequence:
- Schema-level handlers (
onRowUpsert,onRowDelete) are invoked to transform, filter, or route rows before buffering them in a staging database for ordered processing. - After rows are retrieved from the staging database, table-level handlers (
onRowUpsertandonRowDelete, followed byonWrite) are invoked to apply final transformations and custom write logic.
Tip:For details on these handlers and other configuration functions, refer to Userscript API.
- Schema-level handlers (
Commit to target database: Replicator commits the transformed rows to the target database in a single transactional write. Target database writes and logic will only be scheduled to be committed after
onWritereturns, or all table-level handlers are run.
This allows you to precisely defines how data from your source system should look and behave once it reaches your target database, without needing to modify MOLT Replicator's core logic.
Userscripts run in a sandboxed JavaScript runtime inside MOLT Replicator that implements the core ECMAScript language but does not include the extended standard library APIs found in Node.js or web browsers (such as filesystem, networking, or timers). Learn more about userscript limitations.
Usage
To have MOLT Replicator apply a userscript, include the --userscript flag with any Replicator command. The flag accepts a path to a TypeScript filename.
--userscript 'path/to/script.ts'
For example, to apply a userscript named table_filter.ts during PostgreSQL replication:
replicator pglogical \
--sourceConn $SOURCE \
--targetConn $TARGET \
...
--userscript 'table_filter.ts'
Common uses
Userscripts customize the standard behavior of the source change data capture (CDC) stream consumed by Replicator. Common use cases include:
- Renaming columns: Map source column names to different names on the target.
- Row filtering: Filter out specific rows based on conditions, such as excluding soft-deleted records or test data.
- Column filtering: Remove sensitive or unnecessary columns from replicated data.
- Data transformation: Transform column values, compute new columns, or change data types during replication.
- Table partitioning: Distribute rows from a single source table across multiple target tables based on partitioning rules.
- Dead-letter queues: Route failed operations to a separate (DLQ) table for offline inspection and recovery.
For ready-to-use templates that handle the preceding use cases, refer to the userscript cookbook.
Unsupported TypeScript features
Userscripts are TypeScript files that support ECMAScript 5.1, with partial ES6 support.
The JavaScript execution environment in which userscripts run is intentionally minimal. It implements the core ECMAScript language but does not include the extended standard library APIs found in Node.js or web browsers. This ensures that userscripts remain lightweight, deterministic, and focused solely on processing data and executing transactional logic.
The following capabilities are not available within userscripts:
- Filesystem: No file reading or writing, directory listing, file streams, or
fsmodule. - Networking: No HTTP/HTTPS requests, sockets, WebSockets or
fetch. - Process and operating system: No
processobject, environment variables, subprocess execution, or OS-level access. - Timers and scheduling: No
setTimeout/setInterval. - Cryptography and binary utilities: No hashing or HMAC, secure random generation, WebCrypto, or compression or binary buffers.
- Workers and parallelism: No Web Workers, threads, or shared memory.
- Persistent storage: No local/session storage, filesystem-backed persistence, built-in key–value store.
Your IDE will not recognize unsupported functions, and attempting to use any of the preceding features will result in a runtime error.